What Is A Second Order Consumer In A Food Chain What are Secondary Consumers Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy They are placed on the third trophic level in a food
What are the secondary consumers In the following we will show examples of food chains food chains or trophic chains highlighting secondary consumers Is the lion a Secondary consumers are placed at the third trophic level in the food chain These are organisms that eat primary consumers for nutrients energy purposes
What Is A Second Order Consumer In A Food Chain
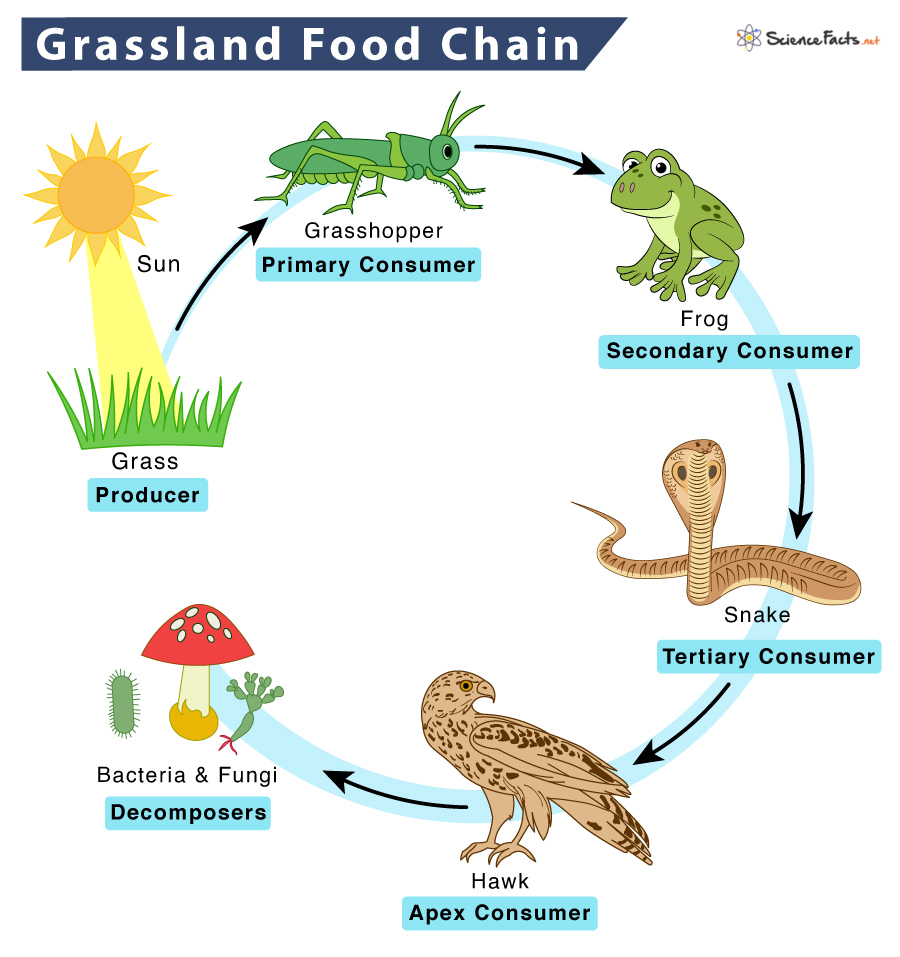
What Is A Second Order Consumer In A Food Chain
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Grassland-Food-Chain.jpg
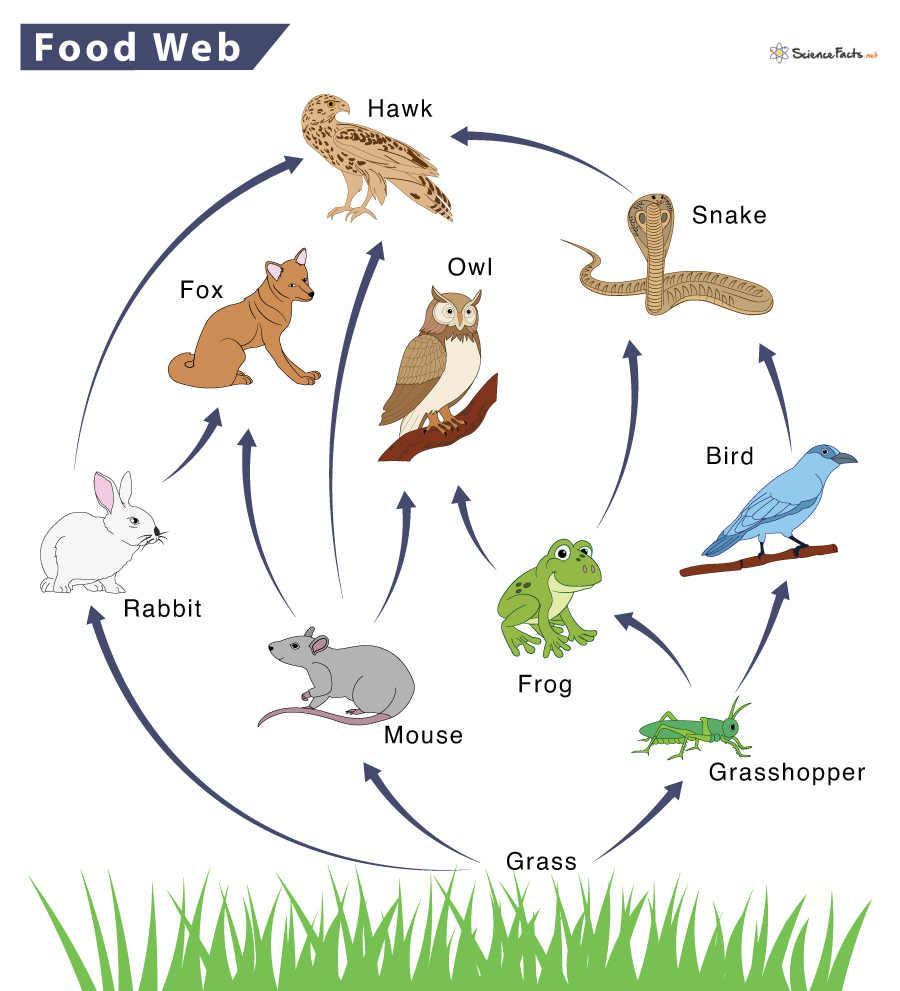
Ecology Jeopardy Template
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Food-Web.jpg
Food Chains Worksheets WorksheetsGO
https://www.worksheetsgo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Food-Chains-Worksheet.jpg
Secondary consumers occupy the third and fourth trophic levels in the food chain and there are two groups of these living organisms omnivores and carnivores The omnivore Humans can be secondary consumers too When someone eats chicken and that chicken was raised eating corn or plants the person becomes a secondary consumer in that chain Chicken primary consumer human
Secondary consumers may be strictly meat eaters carnivores or they may be omnivores eating both plants and animals Third level consumers are any organisms big enough to obtain energy by Arrows in food chains and webs indicate the direction of energy flow from an organism being consumed to the organism consuming it Consumers may be identified by their position in a
More picture related to What Is A Second Order Consumer In A Food Chain
Food In Ecosystems Ecosystems
https://ecosystemgrace.weebly.com/uploads/2/1/3/9/21395256/2696136_orig.jpg
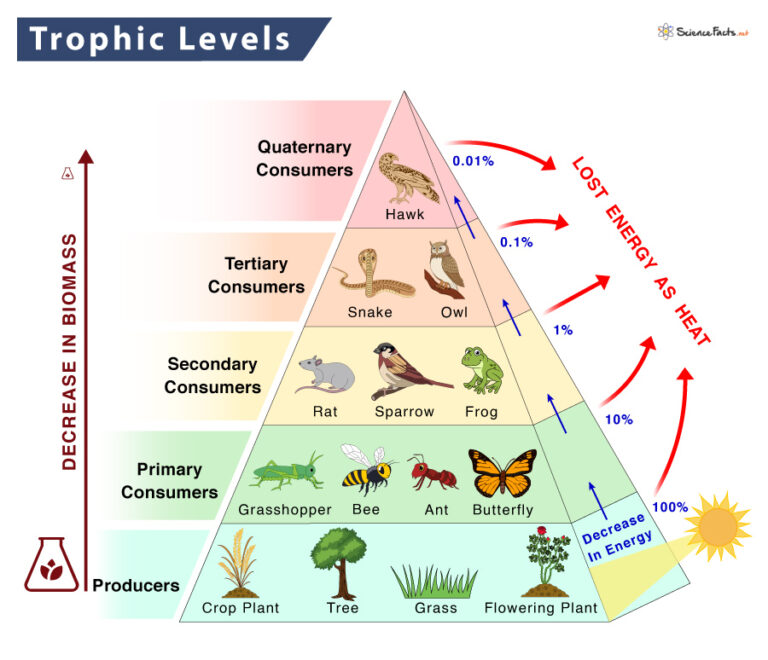
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Trophic-Level-768x660.jpg

Food Chain Definition Geography
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/e7/ed/54/e7ed54135f164814f2f0e47c51f6fcdf.png
In an ecosystem s food chain a secondary consumer is any organism that eats primary consumers Primary consumer examples include cows insects that eat sap or sea What is a secondary consumer in a food chain A secondary consumer is an organism that obtains its energy by consuming primary consumers which are typically
In a food chain the first order consumer holds the position of a herbivore as it solely eats the producer What is a second order consumer The second order consumer feeds off of the first Second order Consumer the organism that eats or derives nutrients from the first order consumer Herbivore a plant eater Carnivore an organism that obtains nutrients from the

Trophic Food Pyramid
https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/656ed910-c5fc-4ecc-8be7-a1861df98afa/trophic-level-pyramid-teachoo-01.jpg
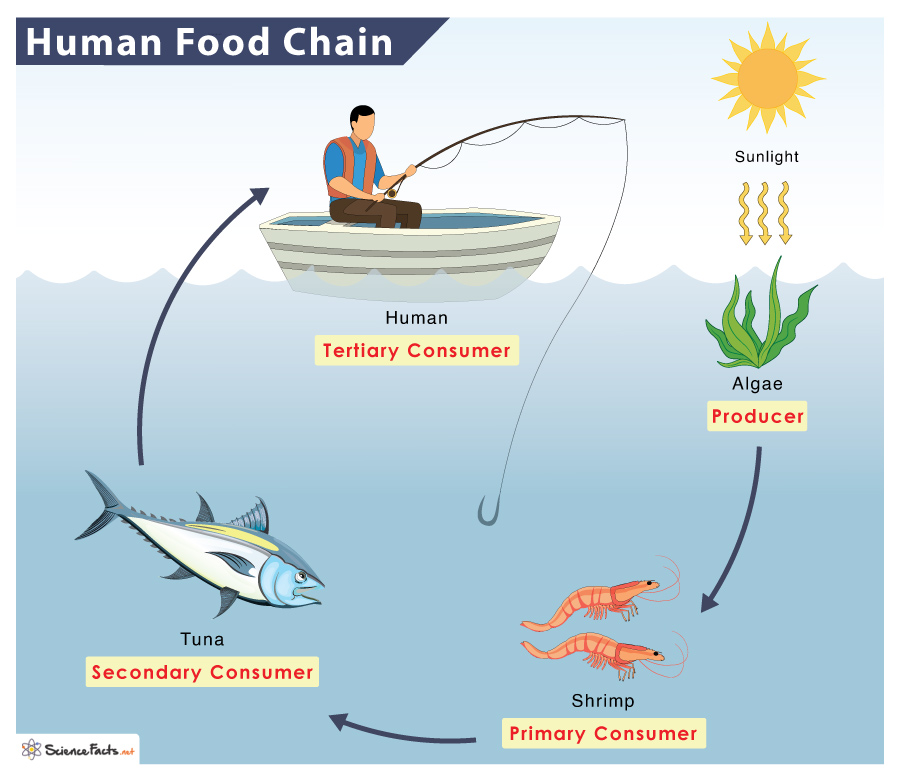
Food Chain Definition Types Examples FAQs At Different
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Human-Food-Chain.jpg

https://microbenotes.com › secondary-con…
What are Secondary Consumers Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy They are placed on the third trophic level in a food

https://agrocorrn.com › secondary-consumers-that-are-and-examples
What are the secondary consumers In the following we will show examples of food chains food chains or trophic chains highlighting secondary consumers Is the lion a
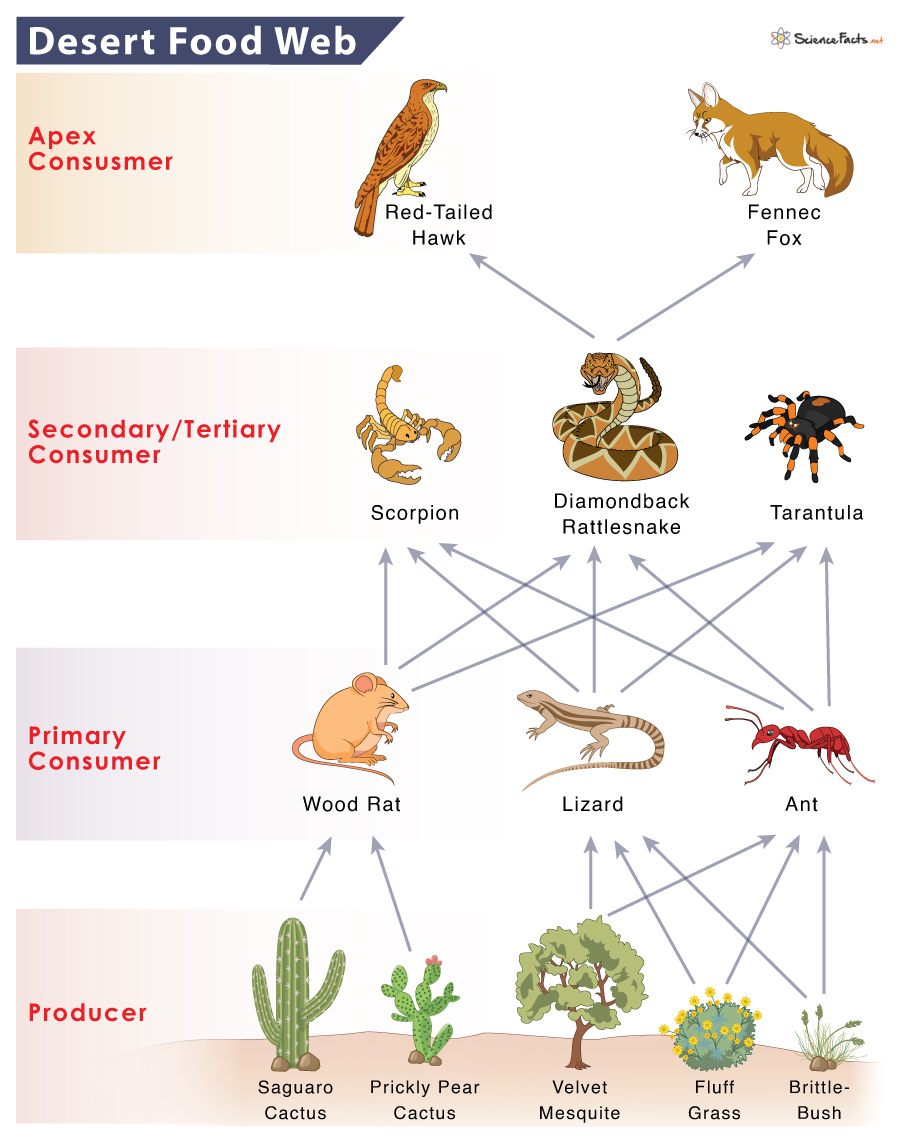
Desert Food Chain Example And Diagram

Trophic Food Pyramid

Arbetsblad F r Klassificering Av Producenter Konsumenter Och Nedbrytare

Rainforest Primary Consumers
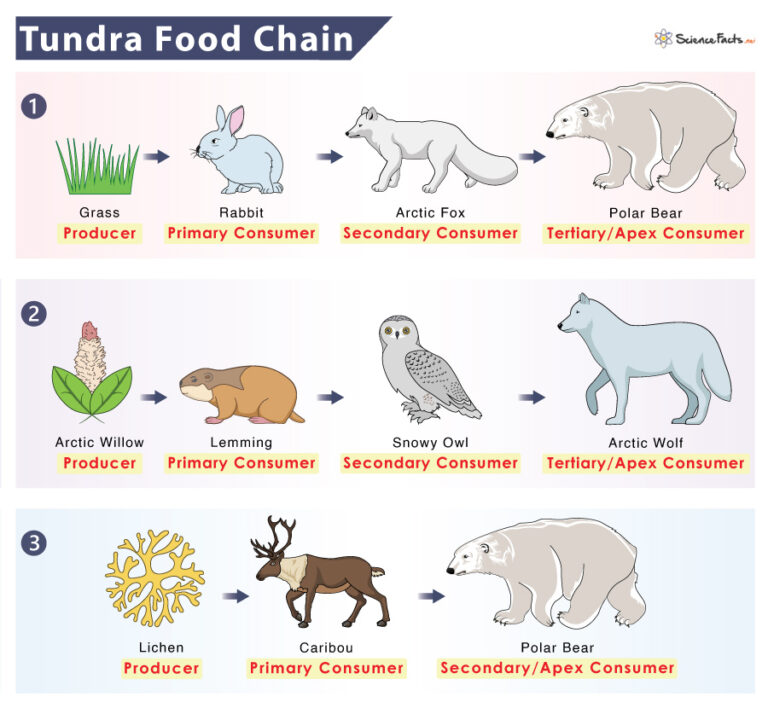
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram
Second World What Is It Countries Examples Vs First World

Second World What Is It Countries Examples Vs First World

Second order Reaction Definition Equations Units Graphs

Human Food Chain

Free Food Webs And Food Chains Worksheet Collection
What Is A Second Order Consumer In A Food Chain - Humans can be secondary consumers too When someone eats chicken and that chicken was raised eating corn or plants the person becomes a secondary consumer in that chain Chicken primary consumer human