How Many Levels Of Consumers Are There In A Food Chain Level 1 Plants and algae make their own food and are called producers Level 2 Herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers Level 3 Carnivores that eat
All food chains end with the apex consumer whose trophic level depends on its prey For example it is at the third trophic level if it consumes a primary consumer If it feeds In most food chains there are no more than five trophic levels People can get more energy by going back one level in the food chain and eating the food that came before
How Many Levels Of Consumers Are There In A Food Chain
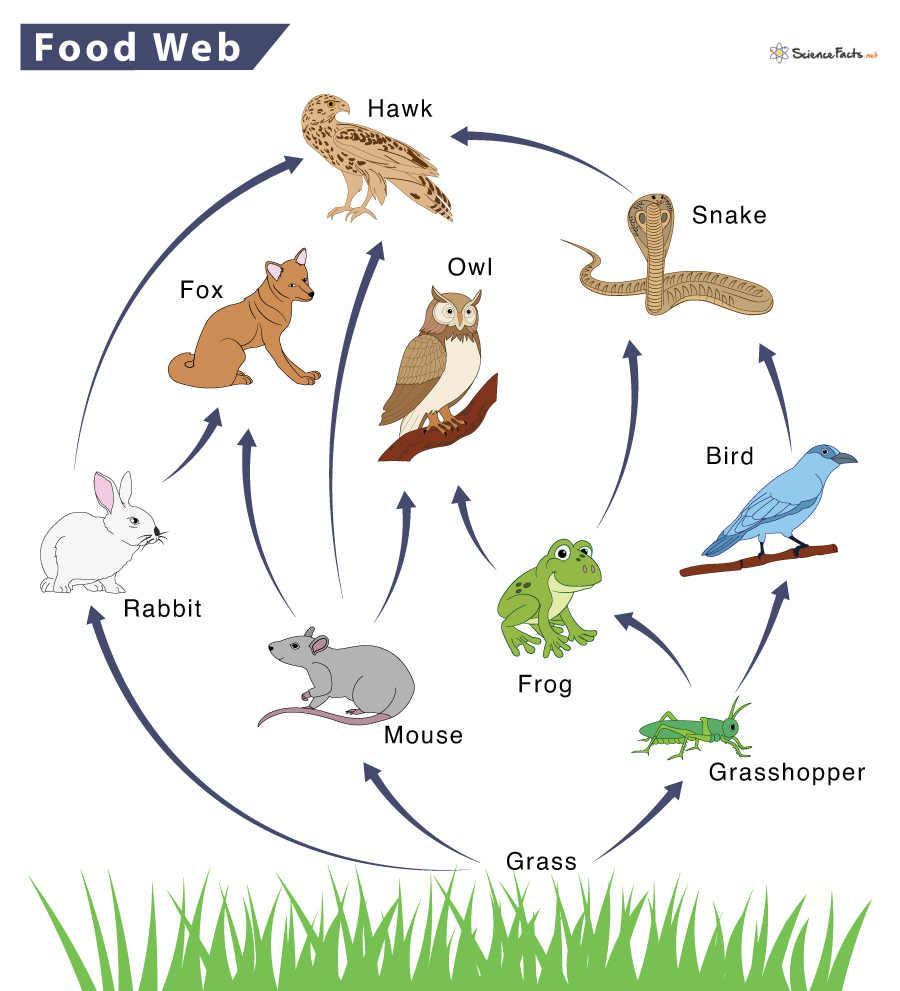
How Many Levels Of Consumers Are There In A Food Chain
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Food-Web.jpg
GRADE 10 UNIT 8 FOOD CHAIN UNIT 8 FOOD CHAIN Read By Par Oo Audio
https://lookaside.fbsbx.com/lookaside/crawler/media/?media_id=473735046800202&get_thumbnail=1
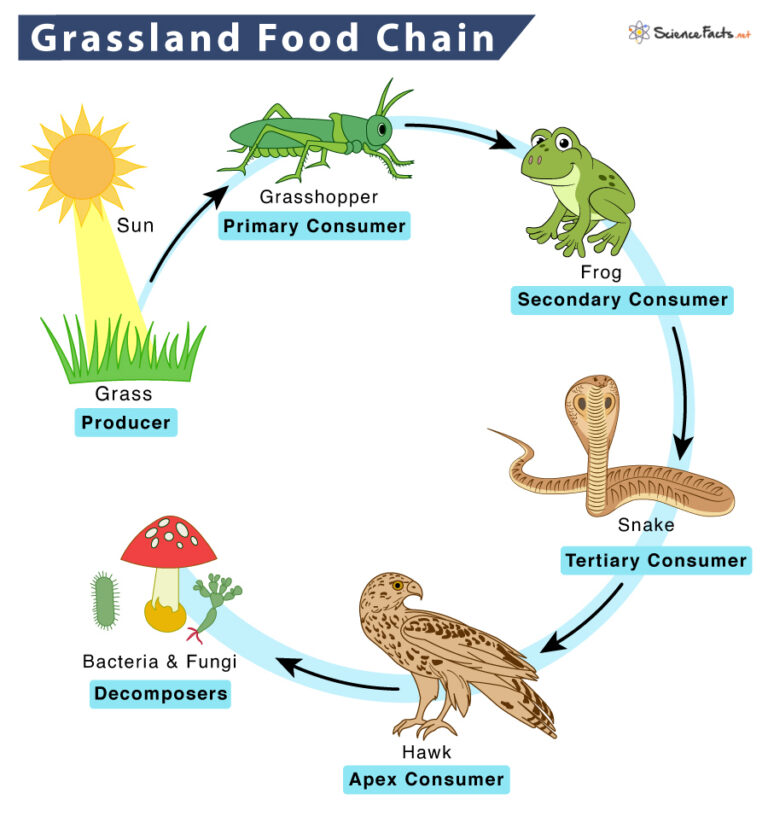
Grassland Food Chain Examples And Diagram
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Grassland-Food-Chain-768x817.jpg
Most food chains have only three or four trophic levels because there is not enough energy remaining at the top of the chain to support more levels The grassland food chain described The movement of organic matter and energy from the producer level through various consumer levels makes up a food chain For example a typical food chain in a
The second level of the food chain is called the Primary Consumer These consume green plants Animals in this group are usually herbivores Examples include insects sheep caterpillars A food chain with four trophic levels will show the feeding relationships of four organisms 1st Trophic Level Producer Makes its own food 2nd Trophic Level Primary Consumer
More picture related to How Many Levels Of Consumers Are There In A Food Chain
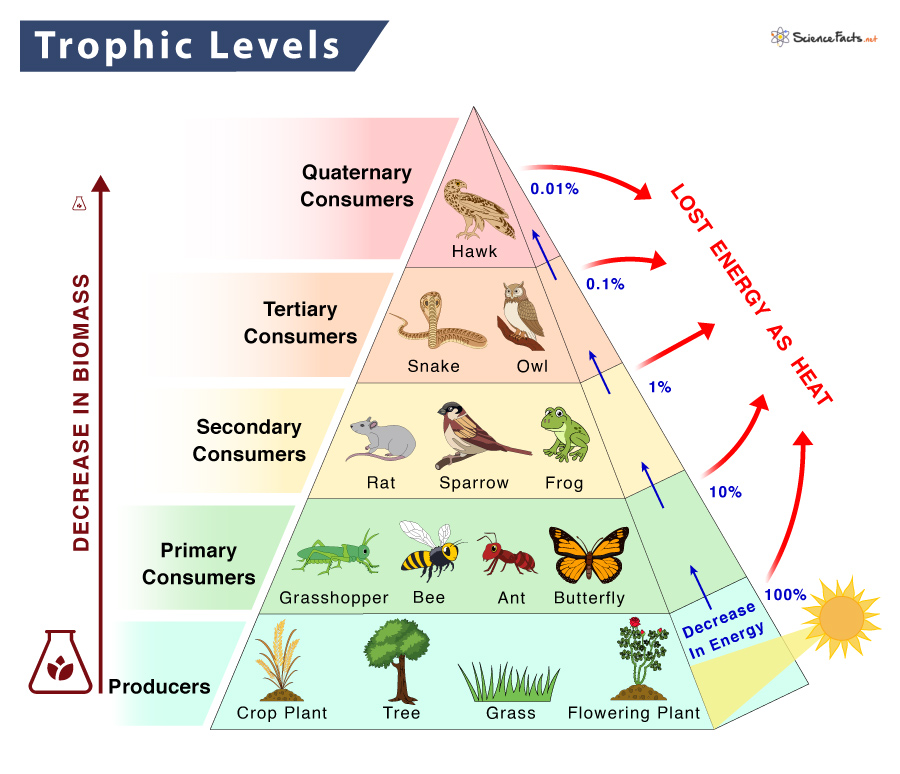
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Trophic-Level.jpg

Some Parts Of The Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/b4/00/74/b4007425194327979fc3dfdec4a9b83e.jpg
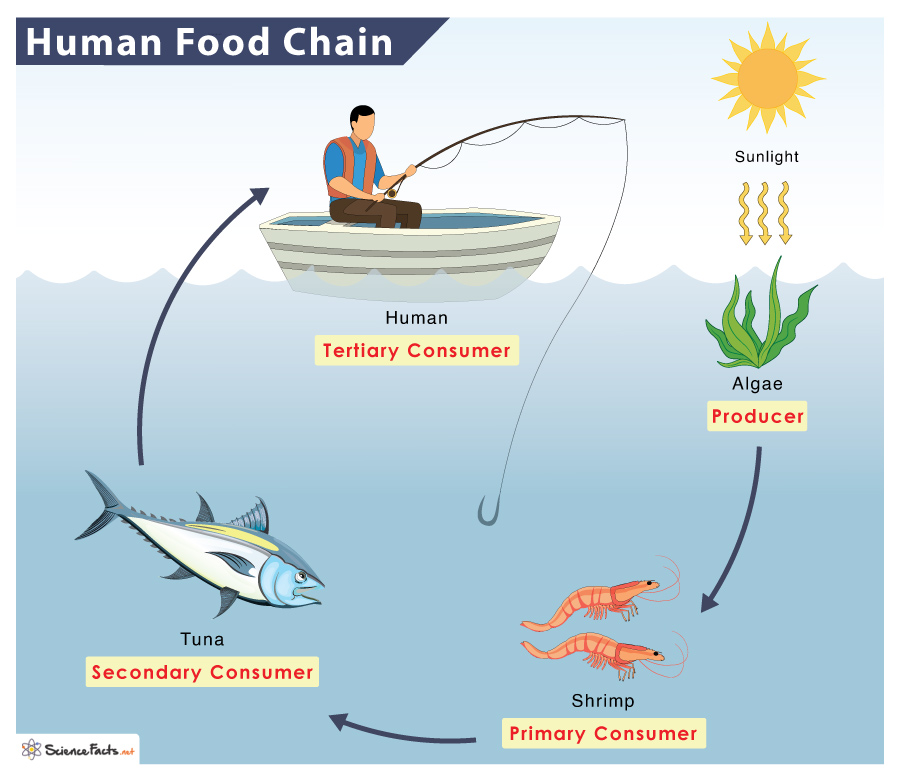
Food Chain Of A Human Examples And Diagram
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Human-Food-Chain.jpg
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another the levels in the food chain are producers primary consumers higher There is a food chain in ecosystems This consists of producers primary consumers secondary consumers and tertiary consumers These are known as trophic levels There are feeding
About 50 of the energy possibly as much as 90 in food is lost at each trophic level when an organism is eaten so it is less efficient to be a higher order consumer than a primary consumer Organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels Roughly speaking these levels are divided into producers first trophic level consumers

Food Chain Definition Types Facts Britannica
https://cdn.britannica.com/35/153035-050-FAF59A2C/food-chain-producers-consumers-decomposers.jpg

Animal Food Chain Stock Photo Alamy
https://c8.alamy.com/comp/2MENRR4/animal-food-chain-2MENRR4.jpg

https://scienceoxygen.com
Level 1 Plants and algae make their own food and are called producers Level 2 Herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers Level 3 Carnivores that eat

https://www.sciencefacts.net › trophic-level.html
All food chains end with the apex consumer whose trophic level depends on its prey For example it is at the third trophic level if it consumes a primary consumer If it feeds
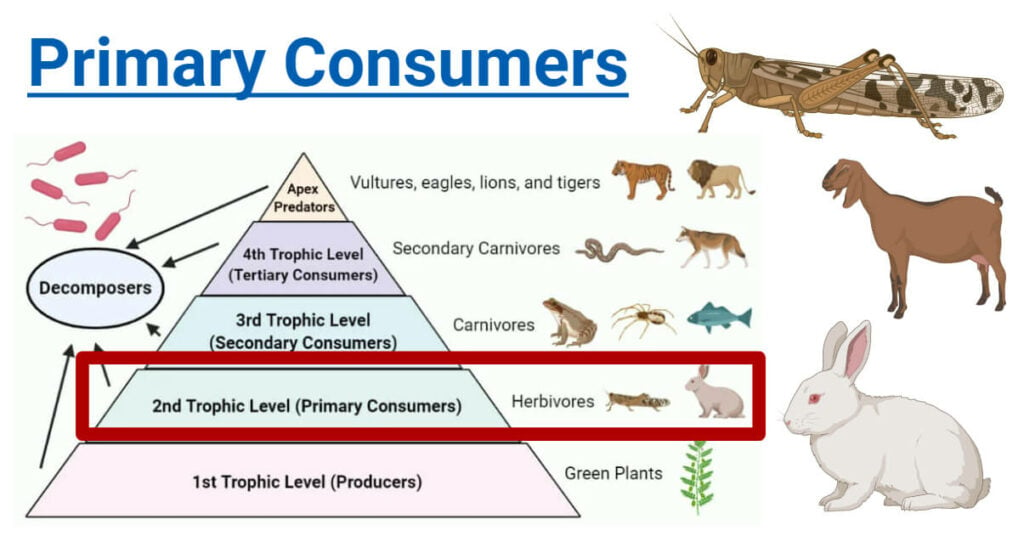
Primary Consumers Definition Food Chain Examples Roles

Food Chain Definition Types Facts Britannica
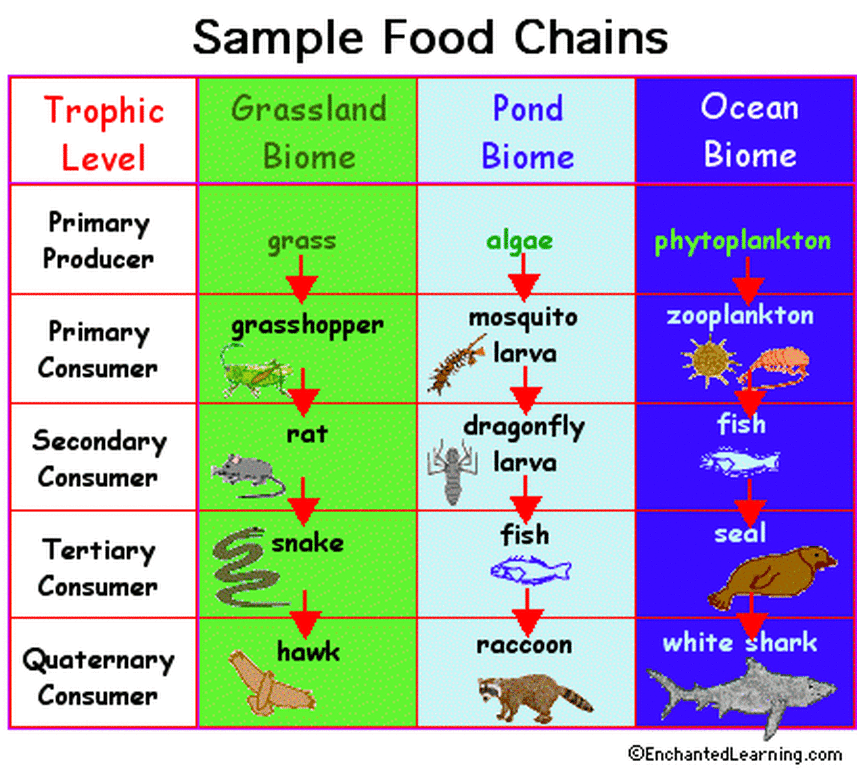
Food Chain And Web Ecology
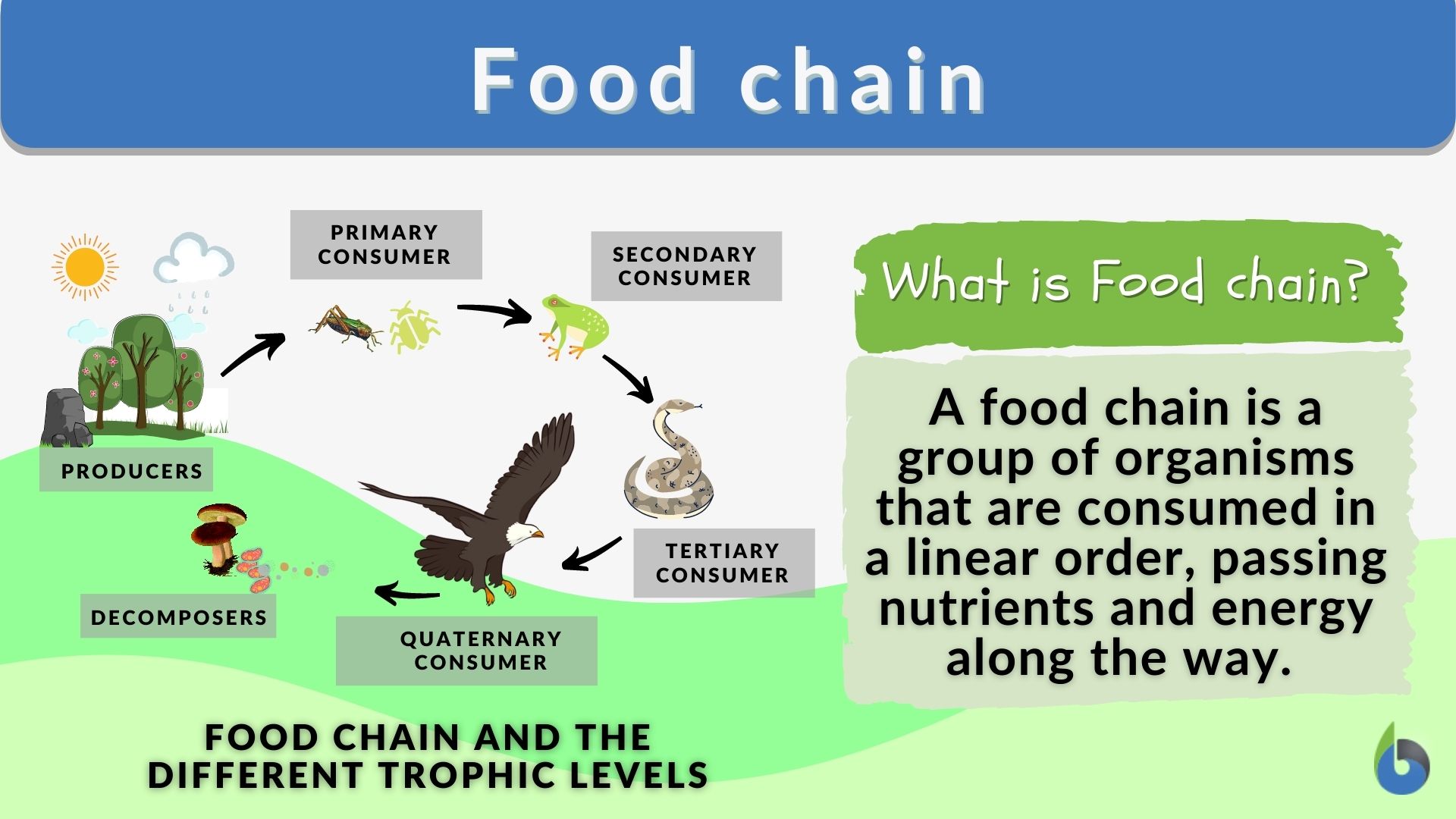
Consumers Examples
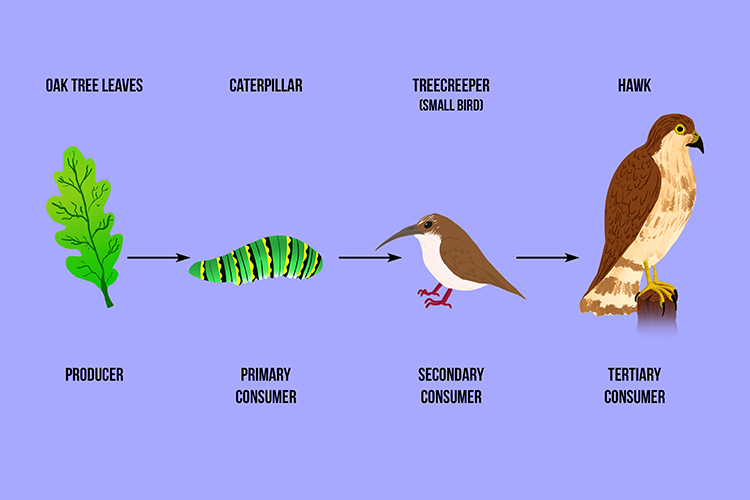
Consumers Examples
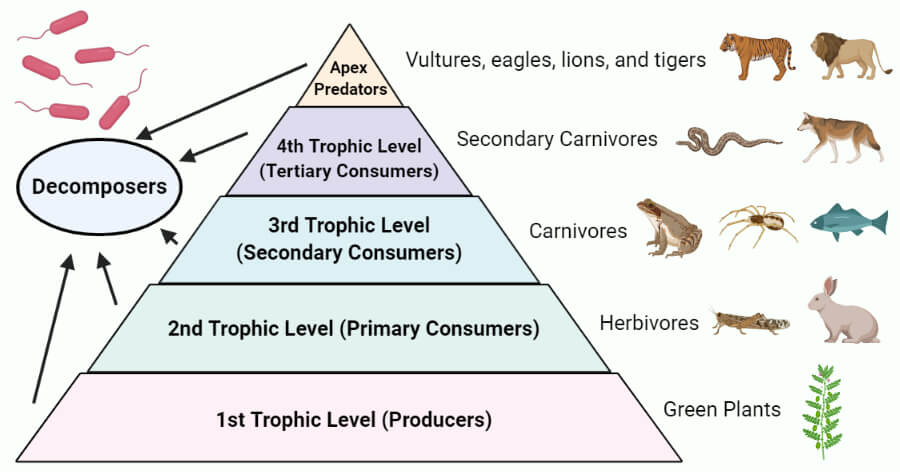
Apex Predators Definition Trophic Cascade Examples

Apex Predators Definition Trophic Cascade Examples

Food Chain Food Web Vocabulary Diagram Quizlet

Trophic Food Pyramid
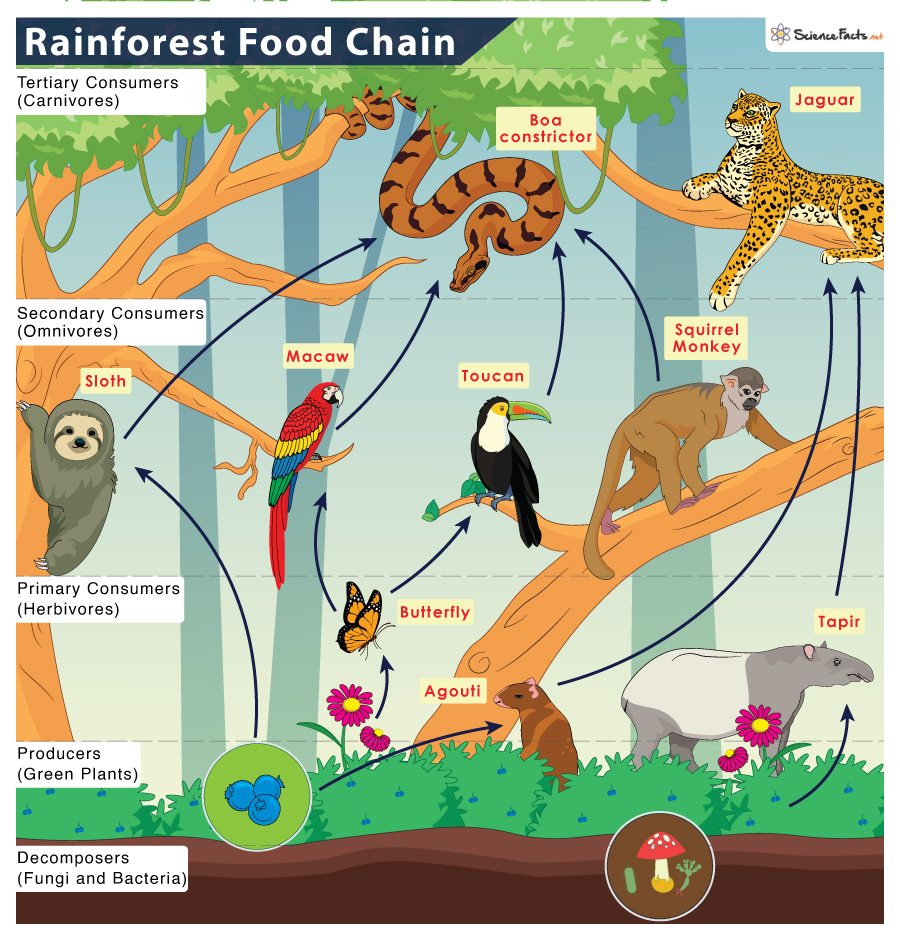
Consumer Animals
How Many Levels Of Consumers Are There In A Food Chain - The second level of the food chain is called the Primary Consumer These consume green plants Animals in this group are usually herbivores Examples include insects sheep caterpillars
