What Eats Decomposers In A Food Web They are associated with the last part of detrital food webs Detritivores such as vultures eat dead plant and animal remains At the same time decomposers like fungi and bacteria turn dead organic matter into
Decomposers Decomposers eat decaying matter like dead plants and animals They help put nutrients back into the soil for plants to eat Examples of decomposers are worms bacteria The food chain is a linear sequence showing energy flow from producers to consumers and decomposers while the food web illustrates multiple interconnected food chains Producers make their food through
What Eats Decomposers In A Food Web
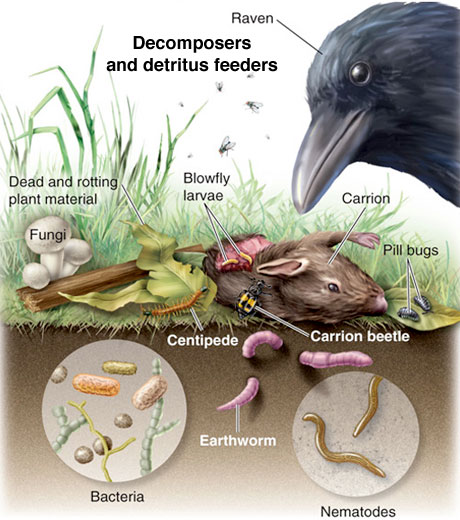
What Eats Decomposers In A Food Web
http://huckleberryfinnclc.weebly.com/uploads/2/7/5/9/27596069/5802620_orig.jpg
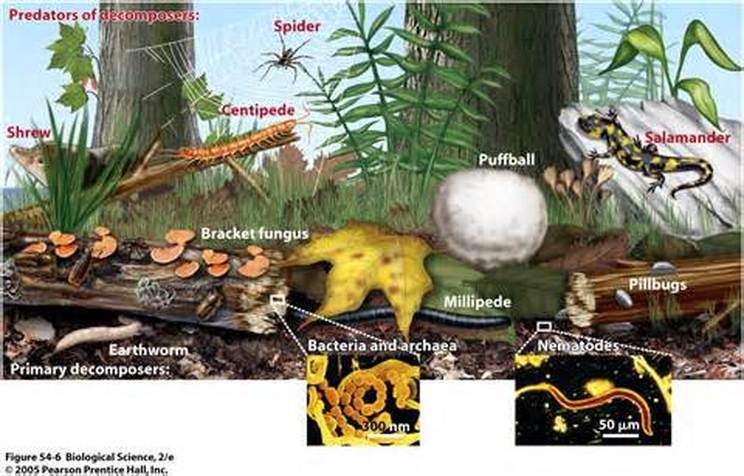
Decomposers Food Chain Cycles
http://huckleberryfinnclc.weebly.com/uploads/2/7/5/9/27596069/1797429.jpg?745
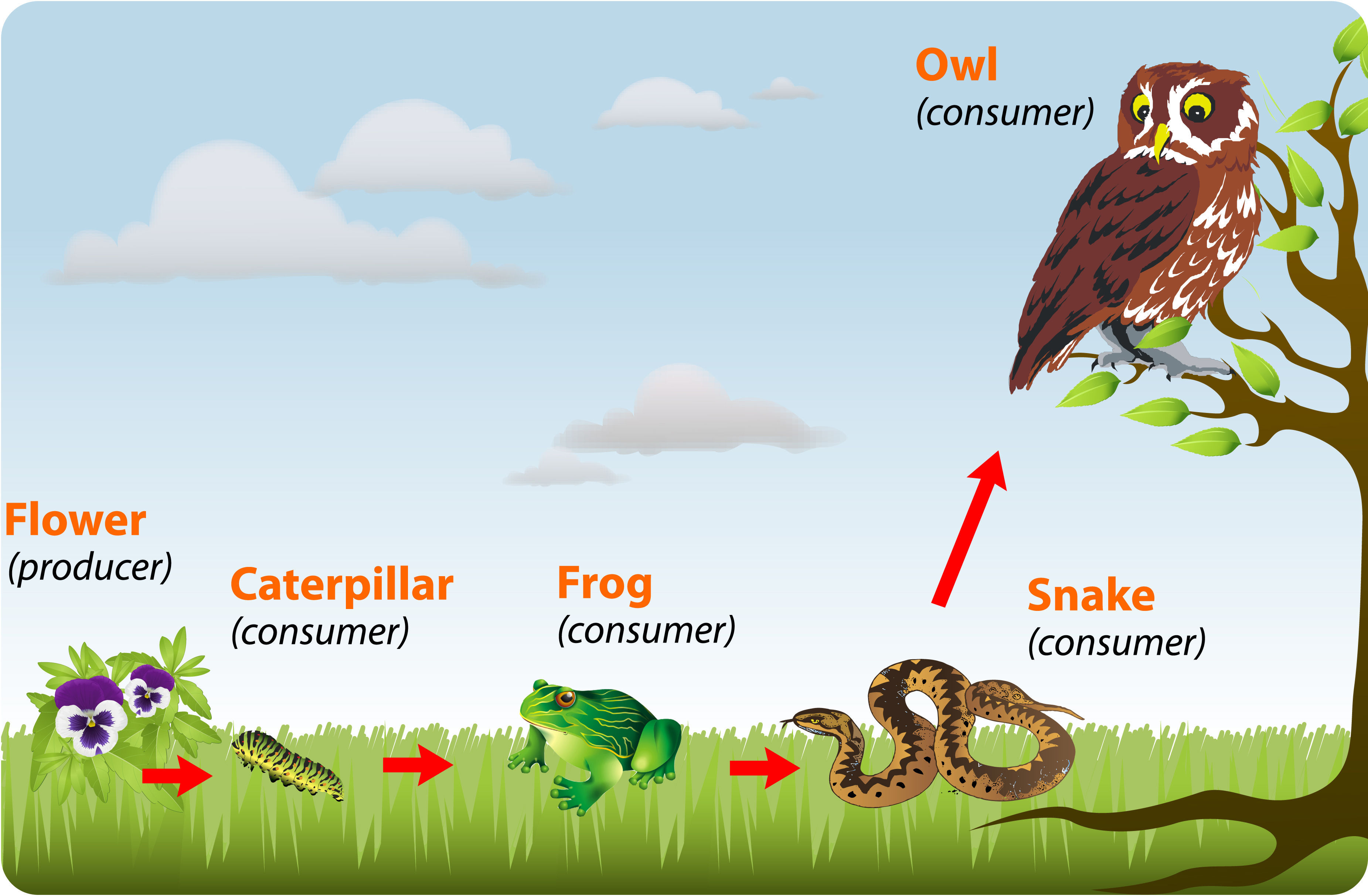
Science Homework
http://hermes.webster.edu/gregoqui/foodchain.jpg
A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem s complex feeding relationships Learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain Without them dead organic matter would accumulate and the flow of energy through the food web would grind to a halt Rather than a typical predator prey relationship
Types of Consumers and Their Impact on Food Web Dynamics IV Decomposers Decomposers are very important in ecosystems because they help with nutrient cycling and keeping ecological balance making them a key A food web is a complex representation of the feeding relationships among organisms within an ecosystem illustrating how energy and nutrients flow through various species It encompasses
More picture related to What Eats Decomposers In A Food Web

Food Web The Tundra Biome
https://idjsstravel.weebly.com/uploads/4/8/7/5/48753251/156314759.jpg?737
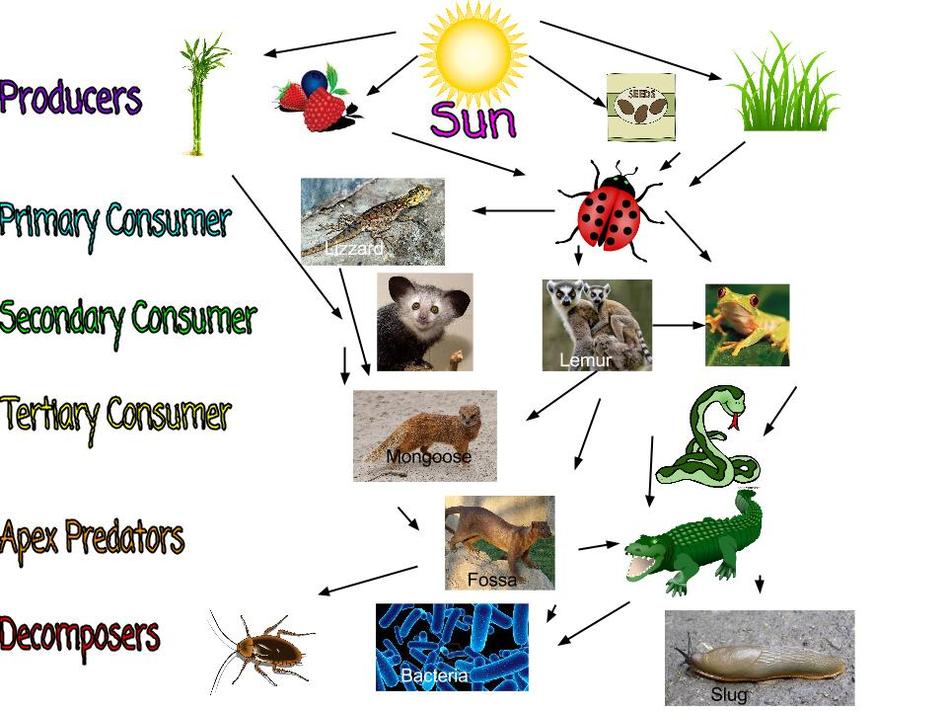
Food Web Makensie
http://aye-aye-aye-aye.weebly.com/uploads/4/5/4/7/45472871/1371569.jpg?950

Food Web MY SITE
http://jordanjarodaldrinplot2.weebly.com/uploads/2/5/2/1/25213360/3059682_orig.png
Food Web Dynamics Decomposition plays a pivotal role in food webs by linking primary producers plants with consumers herbivores and carnivores As dead organic Decomposers Decomposers are organisms that get energy from dead or waste organic material This is the last stage in a food chain Decomposers are an integral part of a food chain as they convert organic waste materials into
Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi mushrooms feed on waste and dead matter converting it into inorganic chemicals that can be recycled as mineral nutrients for plants to Grass is the producer in the grass rabbit fox food chain Photosynthesis provides the energy for most life on Earth A primary consumer eats a producer The rabbit is the primary consumer

Decomposer Biology Britannica
https://cdn.britannica.com/35/153035-050-FAF59A2C/food-chain-producers-consumers-decomposers.jpg
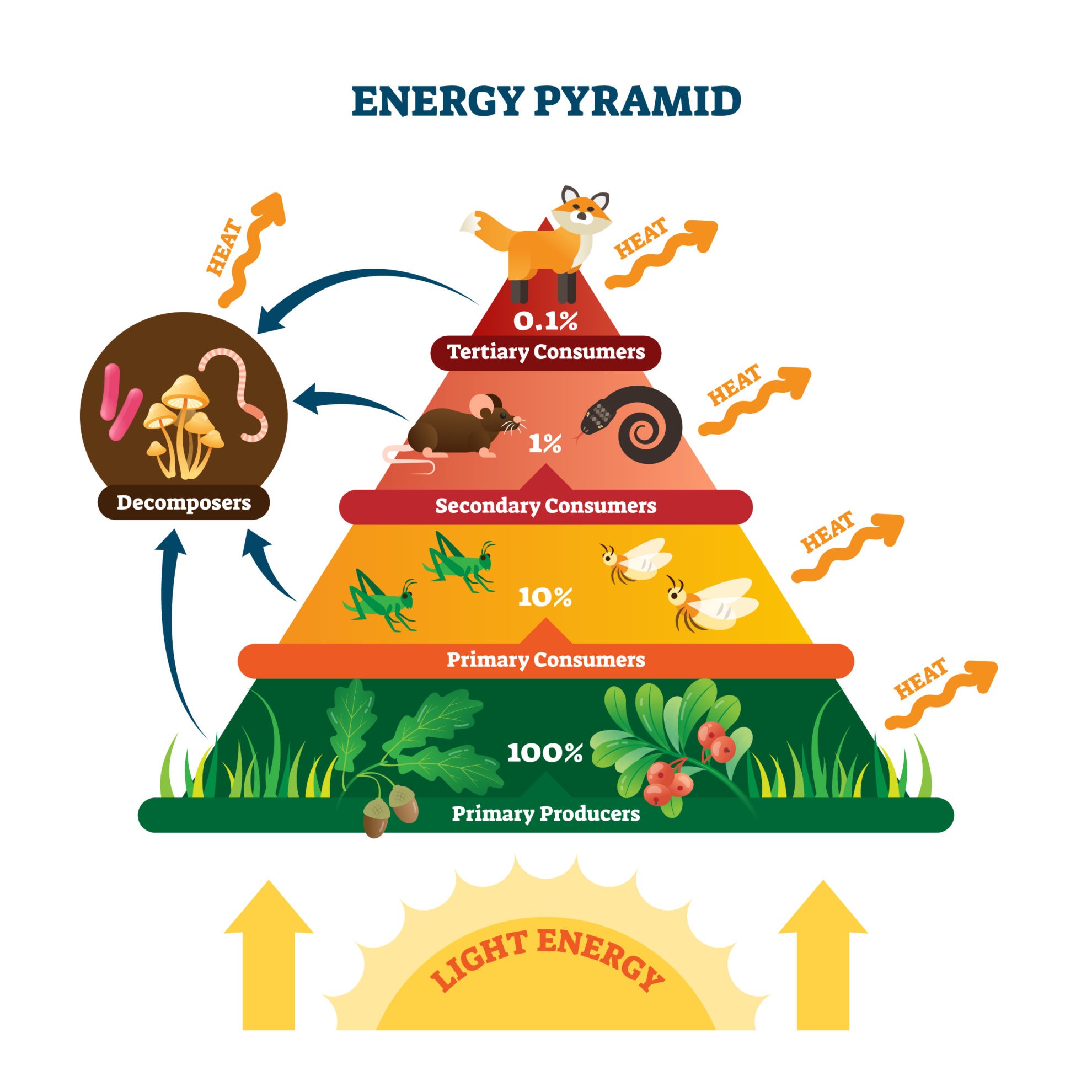
Coelom Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Freshwater-Community-Energy-Relationships-Producers-Consumers.jpg

https://www.sciencefacts.net › food-web.html
They are associated with the last part of detrital food webs Detritivores such as vultures eat dead plant and animal remains At the same time decomposers like fungi and bacteria turn dead organic matter into

https://www.ducksters.com › ... › food_chain_and_web.php
Decomposers Decomposers eat decaying matter like dead plants and animals They help put nutrients back into the soil for plants to eat Examples of decomposers are worms bacteria

Food chain decomposers Food Web Ecosystems Soil

Decomposer Biology Britannica

Decomposer Definition Role Expii
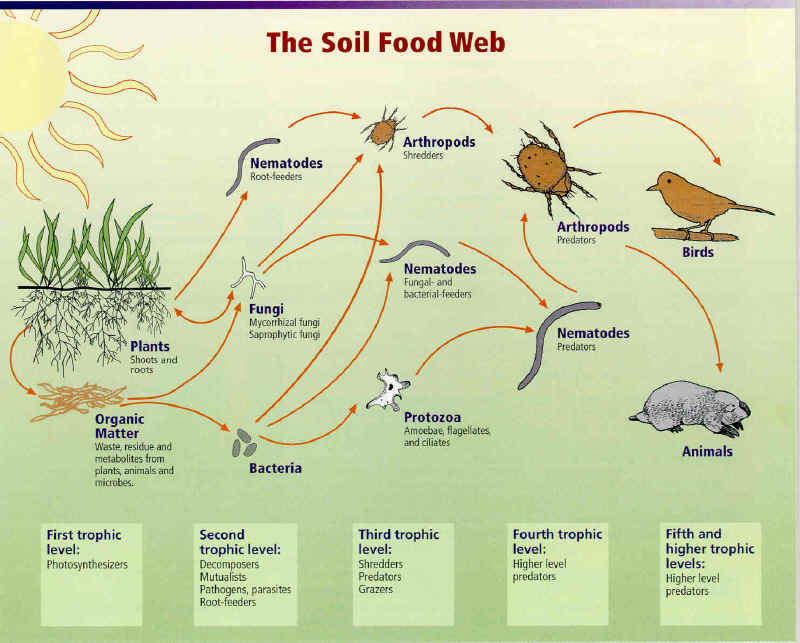
Soil Biology Soil Organic Nutrients Growery Message Board
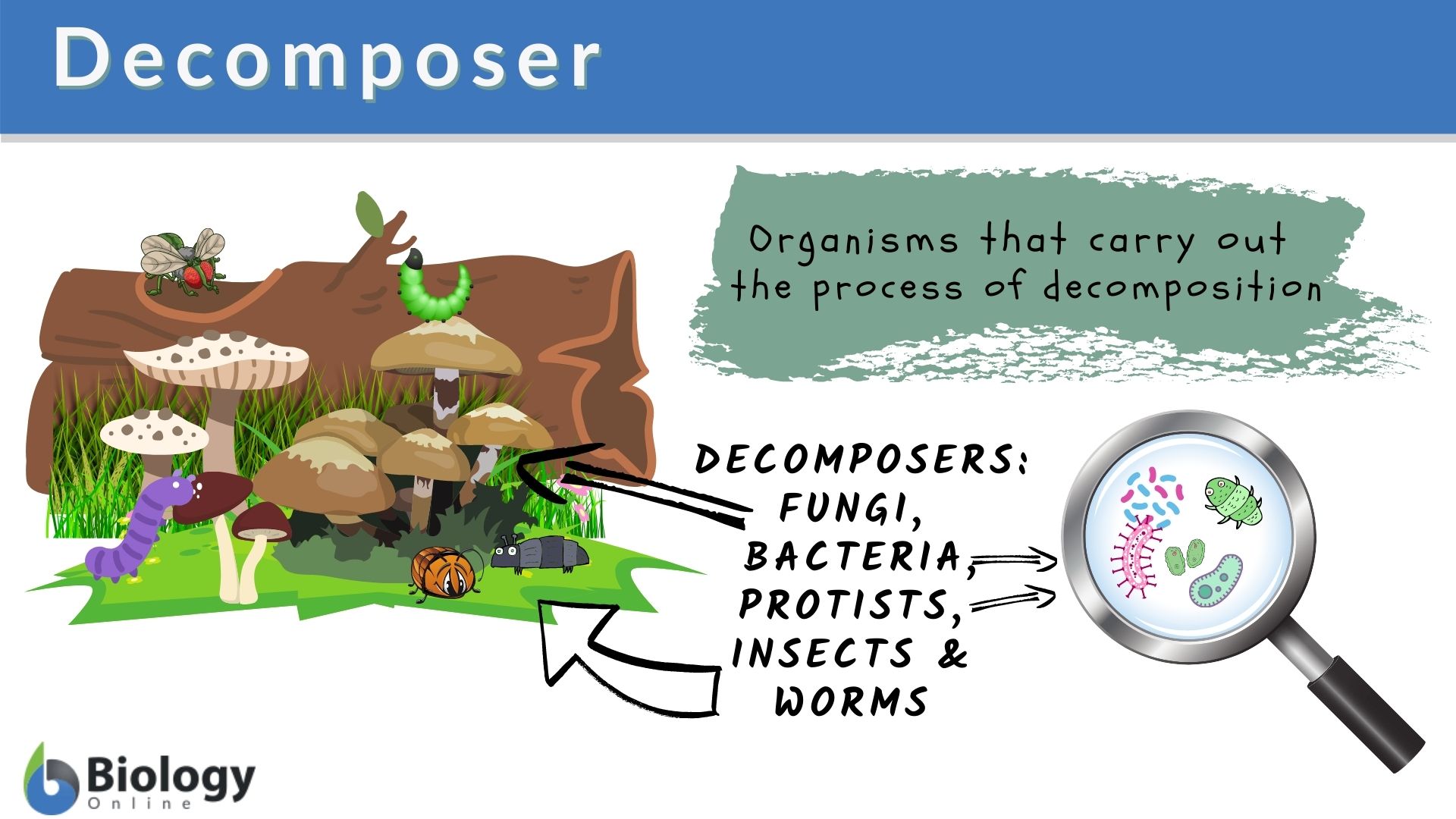
Decomposer Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
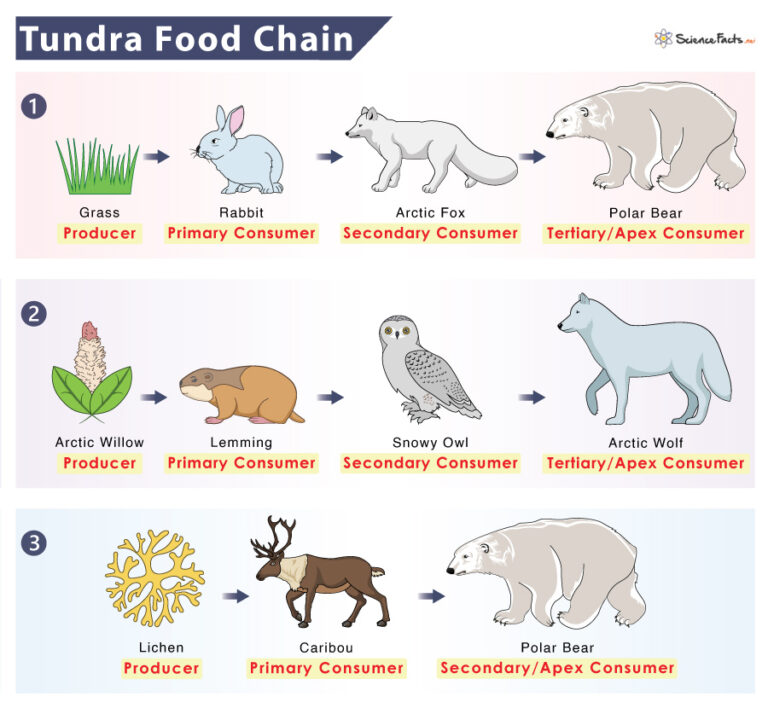
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram

Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram
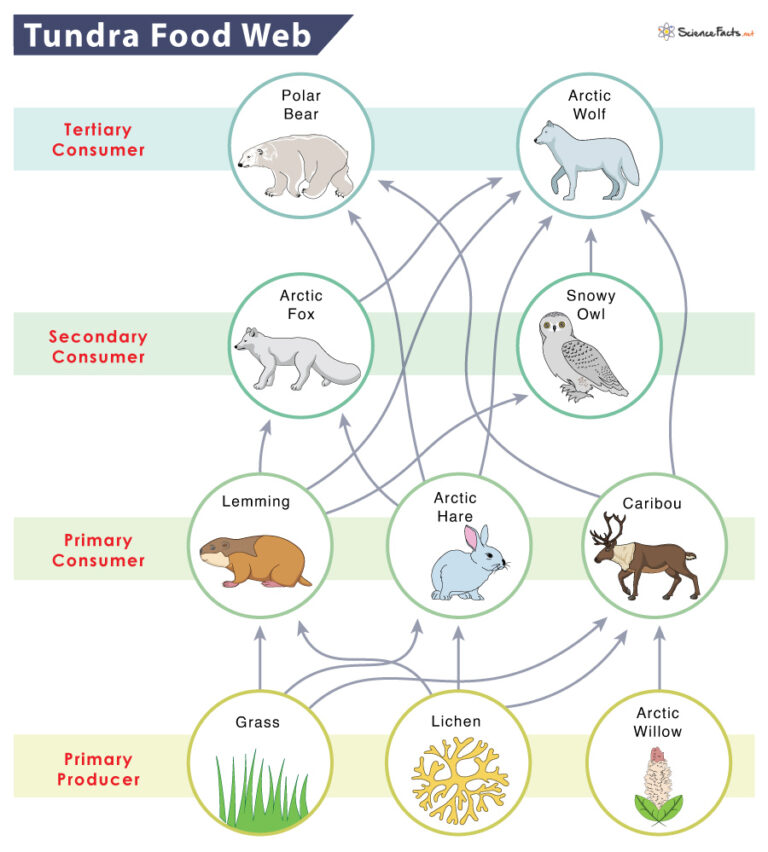
Tundra Food Chain Examples And Diagram

Food Web Introduction

Decomposers Food Chain
What Eats Decomposers In A Food Web - Without them dead organic matter would accumulate and the flow of energy through the food web would grind to a halt Rather than a typical predator prey relationship